FM24C128 データシートの表示(PDF) - Fairchild Semiconductor
部品番号
コンポーネント説明
一致するリスト
FM24C128 Datasheet PDF : 16 Pages
| |||
Write Operations
BYTE WRITE
For byte write operation, two bytes of address are required after
the slave address. These two bytes select 1 out of the 16,384
locations in the memory. The master provides these two address
bytes and for each address byte received, FM24C128 responds
with an acknowledge pulse. Master then provides a byte of data
to be written into the memory. Upon receipt of this data, FM24C128
responds with an acknowledge pulse. The master then terminates
the transfer by generating a stop condition, at which time the
FM24C128 begins the internal write cycle to the memory. While
the internal write cycle is in progress the FM24C128 inputs are
disabled, and the device will not respond to any requests from the
master for the duration of tWR. Refer Figure 4 for the address,
acknowledge and data transfer sequence.
PAGE WRITE
To minimize write cycle time, FM24C128 offers Page Write
feature, which allows simultaneous programming of up to 64
contiguous bytes. To facilitate this feature, the memory array is
organized in terms of “Pages”. A Page consists of 64 contiguous
byte locations starting at every 64-Byte address boundary (for
example, starting at array address 0x0000, 0x0040, 0x0080 etc.).
Page Write operation is confined to a single page. In other words
a Page Write operation will not cross over to locations on the next
page but will “roll over” to the beginning of the same page
whenever end of page is reached and additional data bytes are a
continued to be provided. A Page Write operation can be initiated
to begin at any location within a page (starting address of the Page
Write operation need not be the starting address of a Page).
Page Write is initiated in the same manner as the Byte Write
operation; but instead of terminating the cycle after transmitting
the first data byte, the master can further transmit up to 63 more
bytes. After the receipt of each byte, FM24C128 will respond with
an acknowledge pulse, increment the internal address counter to
the next address, and is ready to accept the next data. If the master
should transmit more than 64 bytes prior to generating the STOP
condition, the address counter will “roll over” and previously
loaded data will be re-loaded. As with the Byte Write operation, all
inputs are disabled until completion of the internal write cycle.
Refer Figure 5 for the address, acknowledge, and data transfer
sequence.
Acknowledge Polling
Once the stop condition is issued to indicate the end of the host’s
write operation, the FM24C128 initiates the internal write cycle.
ACK polling can be initiated immediately. This involves issuing the
start condition followed by the slave address for a write operation.
If the FM24C128 is still busy with the write operation, no ACK will
be returned. If the FM24C128 has completed the write operation,
an ACK will be returned and the host can then proceed with the
next read or write operation.
Write Protection
Programming of the entire memory will not take place if the WP pin
of the FM24C128 is connected to VCC. The FM24C128 will
respond to slave and byte addresses; but if the memory accessed
is write protected by the WP pin, the FM24C128 will not generate
an acknowledge after the first byte of data has been received.
Thus the program cycle will not be started when the stop condition
is asserted.
Byte Write (Figure 4)
S
T
Bus Activity: A
Master R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
WORD
ADDRESS (1)
WORD
ADDRESS (0)
DATA
S
T
O
P
SDA Line
Bus Activity:
EEPROM
A
A
A
A
C
C
C
C
K
K
K
K
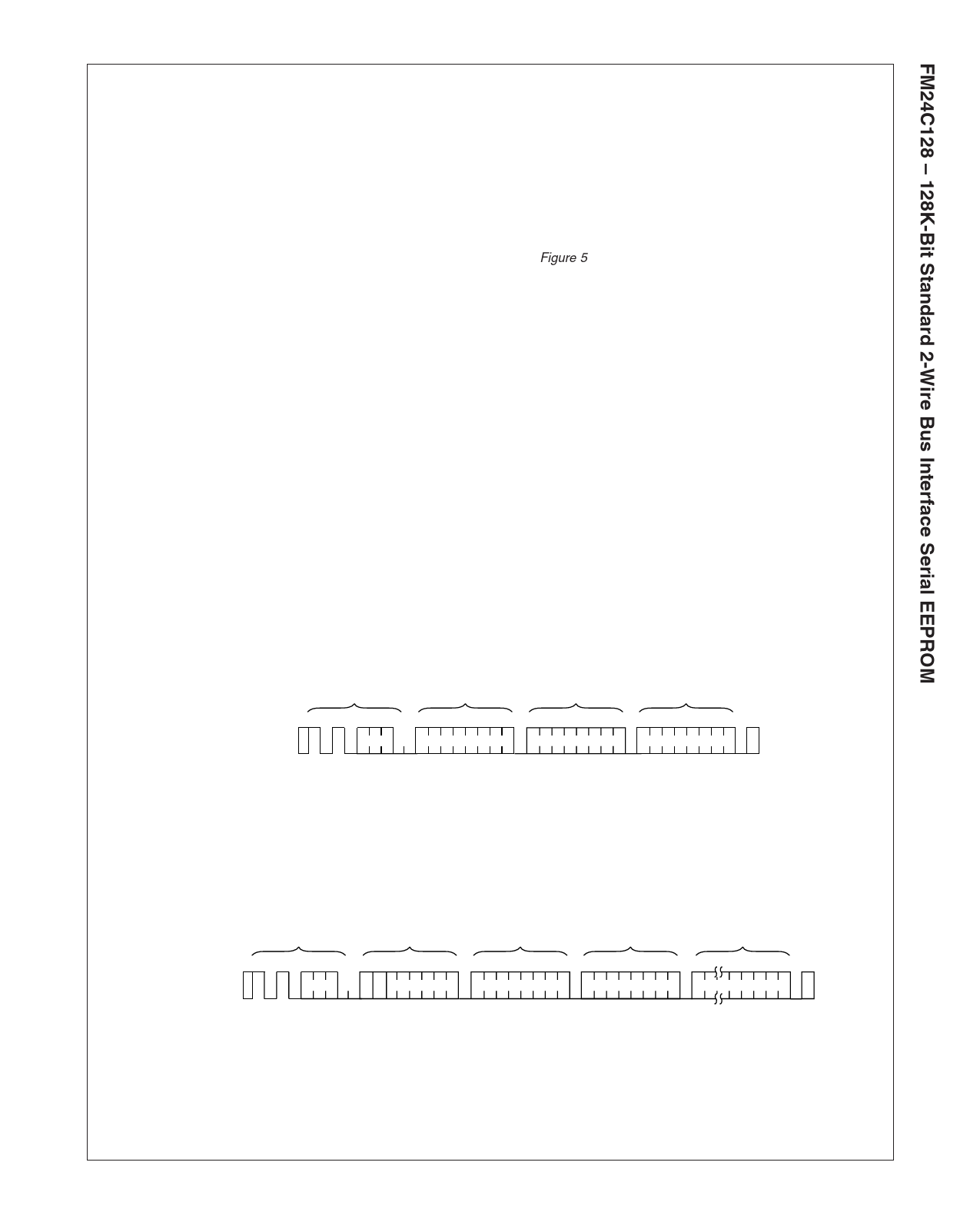
Page Write (Figure 5)
S
T
Bus Activity: A
Master R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
SDA Line 1 0 1 0
Bus Activity
WORD
ADDRESS (1)
WORD
ADDRESS (0)
A
A
C
C
K
K
DATA n
DATA n+63
S
T
O
P
A
A
C
C
K
K
FM24C128 Rev. D
10
www.fairchildsemi.com