VT8237 データシートの表示(PDF) - Unspecified
部品番号
コンポーネント説明
一致するリスト
VT8237 Datasheet PDF : 18 Pages
| |||
VIA VT8237 South Bridge
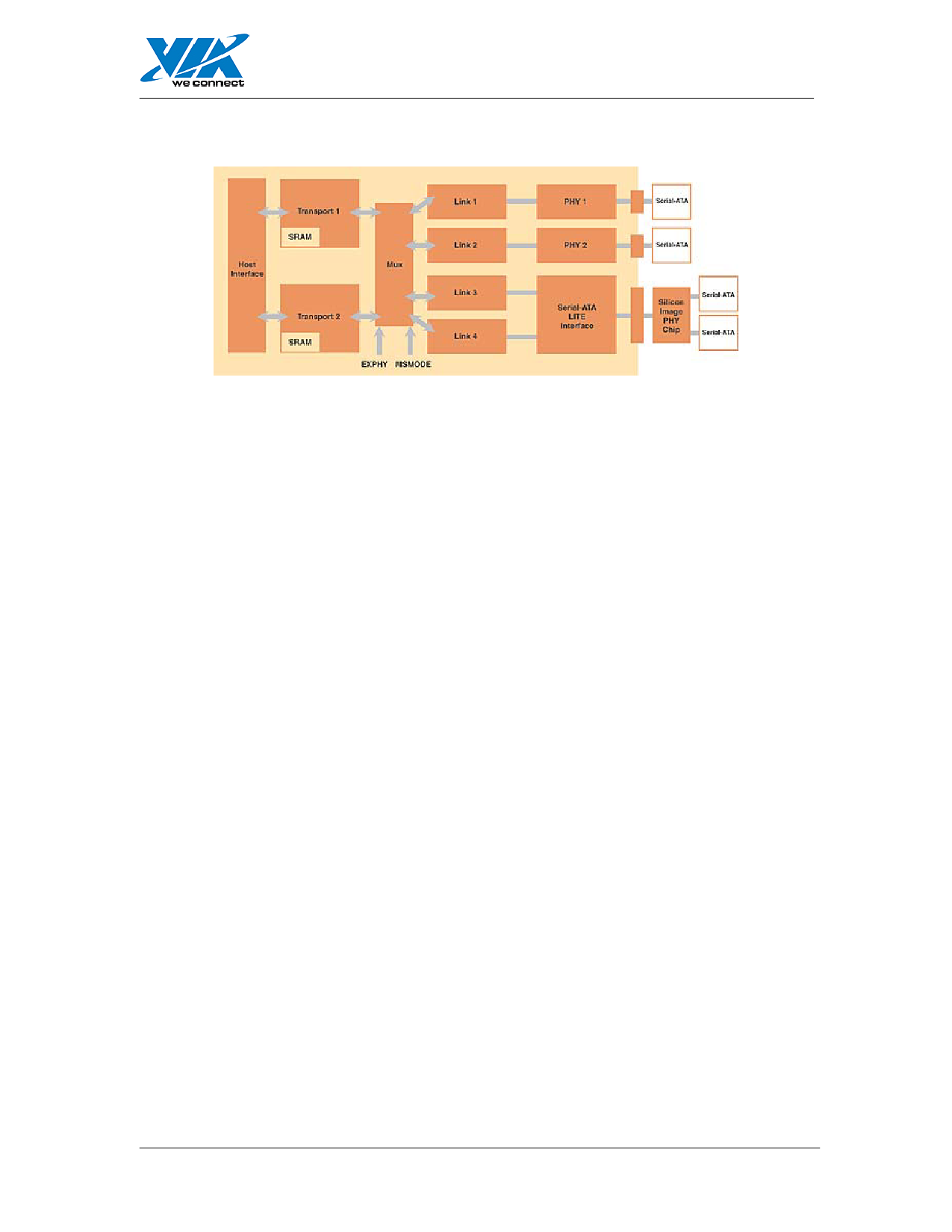
Figure 4: The SATALite Interface
VIA DriveStation™ Parallel ATA-133 Controller
The VIA DriveStation™ Controller Suite also includes an enhanced IDE controller with
a dual channel DMA engine and interlaced dual channel commands, allowing for full
backwards compatibility with up to four Parallel ATA 133/100/66 devices delivering
data transfer rates of up to 133 MB/s.
RAID Explained
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology that harnesses the
power of multiple hard drives working together, and uses advanced data striping and
mirroring techniques to improve data integrity and access speed. Disk arrays are
groups of disk drives that work together to achieve higher data-transfer and I/O
rates than those provided by single large drives. An array is a set of multiple disk
drives plus a specialized controller (an array controller) that keeps track of how data
is distributed across the drives. In Striping, data for a particular file is written in
segments to the different drives in the array rather than being written to a single
drive.
Arrays can also provide Mirroring so that no data is lost if a single drive (physical
disk) in the array should fail. Different RAID ‘levels’ offer varying benefits to users,
for example RAID Level 0 significantly increases hard drive read/write speeds, while
RAID Level 1 provides rock solid data integrity, albeit with a performance trade off
compared to RAID Level 0. The key benefits of each RAID Level are summarized
below:
RAID Level 0 – A RAID 0 or ‘striping’ array organizes data in such a way that
it is striped across the multiple drives, enabling the system to access data
from multiple drives at the same time. The high-speed data access speeds are
especially beneficial for retrieving very large files, such as digital video files,
since they can be spread out effectively across multiple drives and accessed
in more manageable fragments or ‘stripes’. The downside to using RAID Level
0 configurations is that it sacrifices fault tolerance, as no room is made
available to store redundant data.
RAID Level 1 - RAID Level 1 uses a process called disk mirroring to ensure
data reliability, and can also enhance HDD read performance. In a RAID Level
Copyright © VIA Technologies, Inc, 2003.
7
Third party brands and names are the property of their respective owner.